Significantly greater EFS with RYDAPT plus standard chemotherapy compared with standard chemotherapy plus placebo
EFS was the key secondary endpoint in the RATIFY pivotal trial1
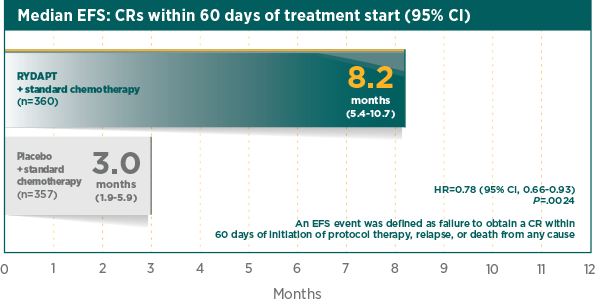
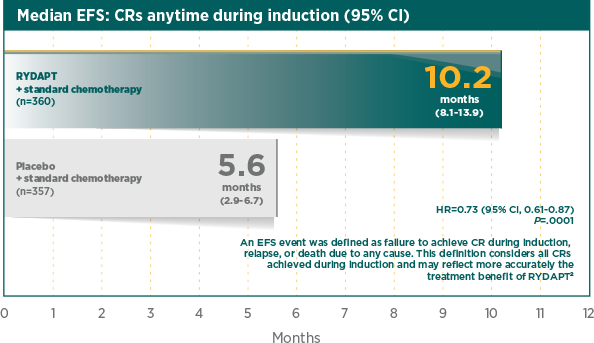
Greater rate of true CR compared with standard chemotherapy plus placebo1
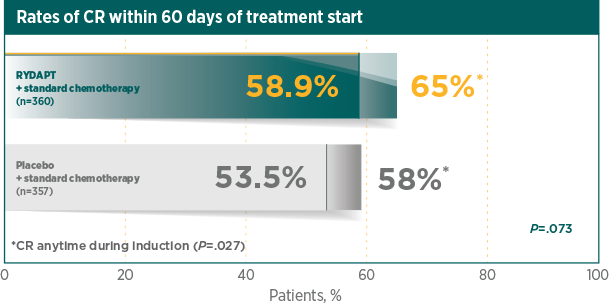
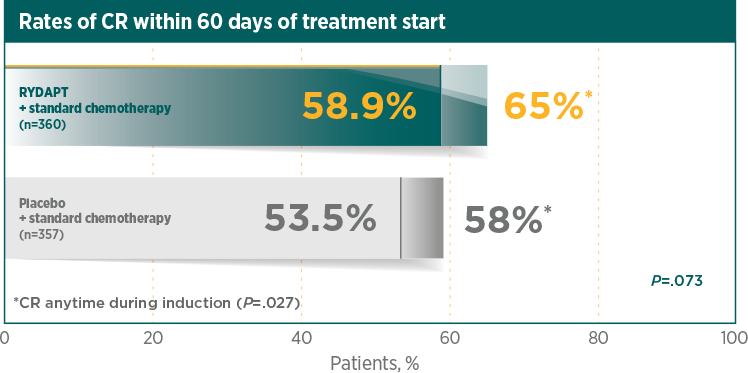
A CR was defined as all of the following, by 60 days after initial induction therapy started, unless otherwise specified in the analysis. Peripheral blood counts: absolute neutrophil count ≥1000/μL, platelet count ≥100,000/μL, no leukaemic blasts in the peripheral blood, adequate erythroid recovery so that red blood cell transfusions are not necessary; bone marrow: adequate cellularity, no Auer rods, <5% blast cells; and no extramedullary leukaemia, such as CNS or soft tissue involvement2
*CR was measured anytime during induction therapy, within and after 60 days1RATIFY was not powered for subgroup analysis by gender and the observed difference for OS by gender cannot be explained. There was no difference by gender for all secondary endpoints1,3
| Endpoint | Overall(95% CI) |
| OS, HR | 0.774(0.629-0.953) |
| EFS (CR induction), HR | 0.728(0.613-0.866) |
| CR induction, OR | 0.743†(0.550-0.1005) |
| DFS (CR induction), HR | 0.663(0.516-0.853) |
| CIR (CR induction), HR | 0.676(0.515-0.888) |
| Endpoint | Males(95% CI) |
| OS, HR | 0.533(0.392-0.725) |
| EFS (CR induction), HR | 0.660(0.506-0.861) |
| CR induction, OR | 0.675†(0.425-1.072) |
| DFS (CR induction), HR | 0.594(0.408-0.865) |
| CIR (CR induction), HR | 0.662(0.436-1.006) |
| Endpoint | Females(95% CI) |
| OS, HR | 1.007(0.757-1.338) |
| EFS (CR induction), HR | 0.825(0.656-1.037) |
| CR induction, OR | 0.824†(0.552-1.230) |
| DFS (CR induction), HR | 0.778(0.554-1.093) |
| CIR (CR induction), HR | 0.742(0.516-1.069) |
Odds ratio calculated as (No CR in treatment/CR in treatment)/(No CR in placebo/CR in placebo).
Significantly longer median DFS with RYDAPT vs placebo1
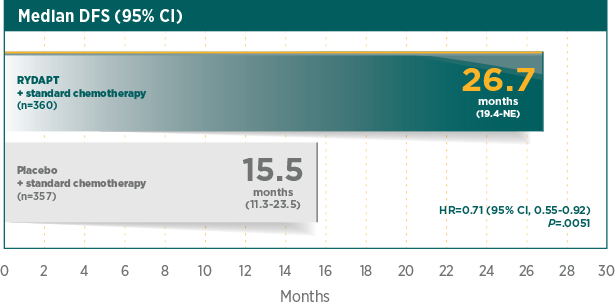
DFS was measured from the date of first CR to the date of relapse or death from any cause2
Decreased rate of median CIR with RYDAPT plus standard chemotherapy1

significant decrease in the risk of relapse with RYDAPT vs placebo1
HR=0.68 (95% CI, 0.52-0.89)
P=.0023
Cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) at 12 months was 26% with RYDAPT plus standard chemotherapy vs 41% for standard chemotherapy plus placebo, in patients who achieved CR during induction1
CI, confidence interval; CIR, cumulative incidence of relapse; CNS, central nervous system; CR, complete remission; DFS, disease-free survival; EFS, event-free survival; HR, hazard ratio; OR, odds ratio; OS, overall survival.
References: 1. RYDAPT [Summary of Product Characteristics]. Novartis Pharma AG; 2017. 2. Data on file. Study no. CPKC412A2301. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; 2016. 3. Stone RM, Mandrekar S, Sanford BL, et al. Midostaurin plus chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia with a FLT3 mutation. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(5):454-464.

