RYDAPT: Assessed in the largest study with all 3 subtypes of advanced SM
RYDAPT was evaluated in 2 open-label, single-arm, multicentre studies of 142 patients with ASM, SM-AHN, and MCL1
RYDAPT was administered orally at 100 mg twice daily until disease progression or intolerable toxicity
The median duration of drug exposure was 11.4 months (range: 0-81 months) in the 2 clinical studies
RYDAPT pivotal study (D2201)1
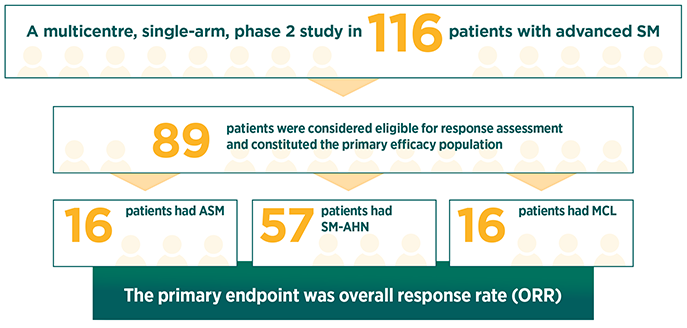
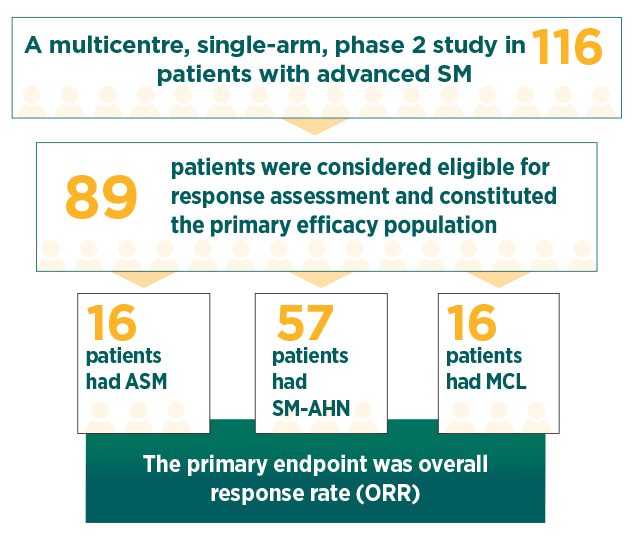
Response rates were assessed based on the modified Valent criteria, and responses were adjudicated by a study steering committee1
35% of patients in the primary efficacy population had 1 C-finding, 22% had 2 C-findings, and 43% had ≥3 C-findings2
The median duration of follow-up was 43 months1
Achieve clinically meaningful, sustained results with RYDAPT
Measurable reduction in organ damage in advanced SM across subtypes1,2
| Overall (N=89) | ASM (n=16) | |
| Primary endpoint: Overall response, % (n) (95% CI) |
59.6% (53)P<.001(48.6-69.8) | 75.0% (12) (47.6-92.7) |
| Major response, % (n) | 44.9% (40) | 62.5% (10) |
| Partial response, % (n) | 14.6% (13) | 12.5% (2) |
| Secondary endpoints: | ||
| Median DOR, months (95% CI) |
18.6(9.9-34.7) | 36.8(5.5-NE) |
| Median OS, months (95% CI) |
26.8(17.6-34.7) | 51.1(28.7-NE) |
| Kaplan-Meier estimates of OS at 5 years, % (95% CI) |
26.1% (14.6-39.2) | 34.8% (1.7-76.2) |
| SM-AHN (n=57) | MCL (n=16) | |
| Primary endpoint: Overall response, % (n) (95% CI) |
57.9% (33) (44.1-70.9) | 50.0% (8) (24.7-75.3) |
| Major response, % (n) | 40.4% (23) | 43.8% (7) |
| Partial response, % (n) | 17.5% (10) | 6.3% (1) |
| Secondary endpoints: | ||
| Median DOR, months (95% CI) |
10.7(7.4-22.8) | NR(3.6-NE) |
| Median OS, months (95% CI) |
20.7(16.3-33.9) | 9.4(7.5-NE) |
| Kaplan-Meier estimates of OS at 5 years, % (95% CI) |
19.9% (8.6-34.5) | 33.7% (12.3-56.8) |
ORR represents the percentage of patients whose best overall response was a major response (defined as complete resolution of ≥1 C-finding) or a partial response (defined as >50% improvement in ≥1 C-finding [good partial response] or as >20% to ≤50% improvement in ≥1 C-finding [minor partial response]).2
Median time to response was 0.3 months (range: 0.1-3.7 months)1
Activity was observed independent of the number of prior therapies and presence or absence of an AHN1
Confirmed responses were observed in both KIT D816V mutation–positive patients (ORR 63%) and patients with KIT D816V wild-type or unknown mutation status (ORR 43.8%)1
46% of patients had a decrease in bone marrow infiltration that exceeded 50%1
58% had a decrease in serum tryptase levels that exceeded 50%1
68.9% of patients had spleen volume decrease by ≥10% in at least 1 postbaseline assessment (26.7% of patients had a reduction of ≥35%, which correlates with a 50% decrease by palpation)1
Demonstrated efficacy across all 3 subtypes of advanced SM
Post hoc exploratory efficacy analysis per IWG-MRT-ECNM consensus criteria1*
| All patientsevaluated(N=113) | ASM(n=15) | |
| Overall response rate, % (n) (95% CI) |
28.3% (32)(20.2-37.6) | 60% (9)(32.3-83.7) |
| Best overall response, % (n) | ||
| Complete remission | 0.9% (1) | 0% |
| Partial remission | 15% (17) | 33.3% (5) |
| Median DOR, months (95% CI) |
NE(27-NE) | 36.8(10.3-36.8) |
| OS rate, % | 57.5% | 26.7% |
| Median OS, months (95% CI) |
29.9(20.3-42.0) | 51.1(34.7-NE) |
| SM-AHN(n=72) | MCL(n=21) | |
| Overall response rate, % (n) (95% CI) |
20.8% (15)(12.2-32.0) | 33.3% (7)(14.6-57.0) |
| Best overall response, % (n) | ||
| Complete remission | 0% | 4.8% (1) |
| Partial remission | 11.1% (8) | 14.3% (3) |
| Median DOR, months (95% CI) |
NE(17.3-NE) | NE(4.1-NE) |
| OS rate, % | 68.1% | 57.1% |
| Median OS, months (95% CI) |
22.1(16.8-32.2) | 22.6(8.3-NE) |
| Subtype unknown(n=5) | |
| Overall response rate, % (n) (95% CI) |
20% (1)(0.5-71.6) |
| Best overall response, % (n) | |
| Complete remission | 0% |
| Partial remission | 20% (1) |
| Median DOR, months (95% CI) |
NE |
| OS rate, % | 0% |
| Median OS, months (95% CI) |
NE |
Response to RYDAPT was determined using a computational algorithm applied without any adjudication. Out of 116 patients, 113 had a C-finding as defined by IWG response criteria (excluding ascites as a C-finding). All responses were considered and required a 12-week confirmation. Patients who received non-study antineoplastic therapy were censored at the time of the new therapy.1
The RYDAPT supportive study (A2213) was a single-arm, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study of 26 patients with advanced SM1
The primary endpoint was ORR evaluated by the Valent criteria during the first 2 cycles of treatment
The median duration of follow-up was 73 months
Responses for patients with advanced SM in the supportive study:
73% of patients (19 of 26) achieved a response in the first 2 cycles of treatment1
Supportive study: a single-arm, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial of 26 patients with advanced SM (A2213). RYDAPT was administered orally at 100 mg twice daily in 28-day cycles. The primary endpoint was ORR evaluated by the Valent criteria during the first 2 cycles of treatment. The median duration of follow-up was 73 months, and the median DOR was not reached. Median OS was 40.0 months (patients were only followed for 1 year after treatment discontinuation for survival).1
ASM, aggressive systemic mastocytosis; CI, confidence interval; DOR, duration of response; ECNM, European Competence Network on Mastocytosis; IWG-MRT, International Working Group-Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Research and Treatment; MCL, mast cell leukaemia; NE, not estimated; NR, not reached; OS, overall survival; SM-AHN, systemic mastocytosis with an associated haematological neoplasm.
References: 1. RYDAPT [Summary of Product Characteristics]. Novartis Pharma AG; 2017. 2. Gotlib J, Kluin-Nelemans HC, George TI, et al. Efficacy and safety of midostaurin in advanced systemic mastocytosis. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(26):2530-2541.

